Source Generators 探索
1. 前言
博主在FireUG社区分享了该主题, 具体视频如下:
链接地址: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1XR4y177L2?p=2
2. 什么是Source Generators
- Source Generator是在编译期间运行的一段代码,它可以在编译期间生成代码, 并与与其余代码一起编译
- 伴随着C# 9发布
- .NET Standard 2.0 组件
3. 原理图
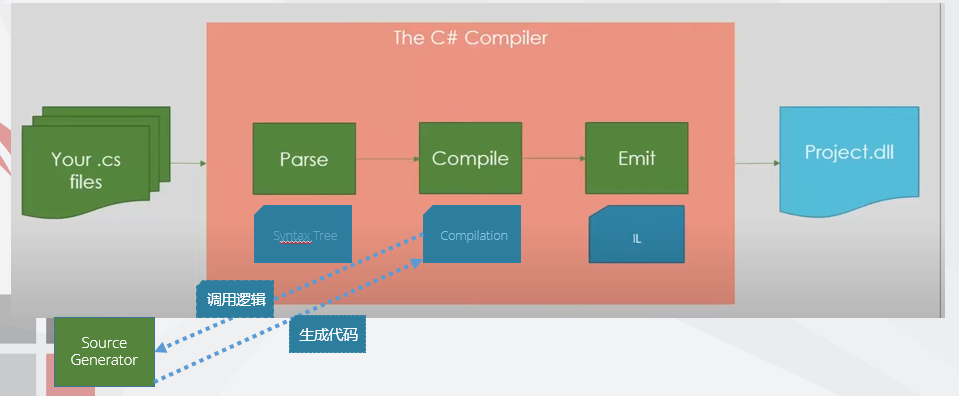
3. 常见问题
3.1 是否会真实生成文件?
默认不生成文件, 但是可以通过属性 EmitCompilerGeneratedFiles 来生成真实文件
3.2 是否支持修改现有类中的代码?
不支持
3.3 Source Generators的优势?
- 编译时替换了运行时, 性能的巨大提升
- 相对于Emit的实现方式, 代码更加友好,可读性更高
- 相对于AOP, 有更丰富的”连接点”
- 可以采用”特殊”的方式,实现对原有逻辑的”修改”
3.4 如何采用”特殊”的方式,实现对原有逻辑的”修改”
- 部分类(partial Class)
- 隔离用户代码和自动生成的代码
- 不同的部分类可以直接互相访问其成员
- 部分类类名必须相同
- 部分方法(partial methods)
- 2007年左右,随着C# 3.0的发布
- 各文件中同一个partial method的函数声明必须一致
- partial methods不能有返回值
- partial methods不能接受out参数
- 不能在partial methods的声明上添加访问级别修饰符, partial methods都是private的
- 新的部分方法(partial methods)
- 和Source Generators一起, 随着C# 9.0的发布,
- partial methods可以有返回值
- partial methods可以接受out参数
- 可以在partial methods的声明上添加访问级别修饰符
- 但是,必须要实现该方法
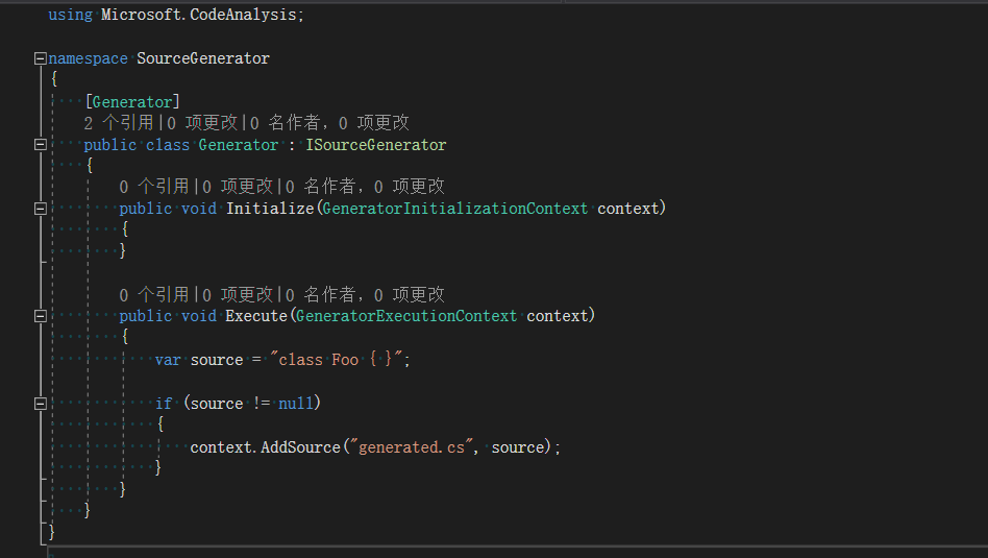
4. 如何使用
5. 如何调试
- Debugger.Launch()
- (推荐)GeneratorDriver类
- 单元测试
- 控制台方法
5.1 调试示例, 特别注意 CSharpGeneratorDriver
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string source = @"
namespace Foo
{
class C
{
void M()
{
}
}
}";
var (diagnostics, output) = GetGeneratedOutput(source);
if (diagnostics.Length > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Diagnostics:");
foreach (var diag in diagnostics)
{
Console.WriteLine(" " + diag.ToString());
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Output:");
}
Console.WriteLine(output);
}
private static (ImmutableArray<Diagnostic>, string) GetGeneratedOutpu(string source)
{
var syntaxTree = CSharpSyntaxTree.ParseText(source);
var references = new List<MetadataReference>();
Assembly[] assemblies = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies();
foreach (var assembly in assemblies)
{
if (!assembly.IsDynamic)
{
references.Add(MetadataReference.CreateFromFile(assembly.Location));
}
}
var compilation = CSharpCompilation.Create("foo", new SyntaxTree[] { syntaxTree }, references,
new CSharpCompilationOptions(OutputKind.DynamicallyLinkedLibrary));
ISourceGenerator generator = new Generator();
var driver = CSharpGeneratorDriver.Create(generator);
driver.RunGeneratorsAndUpdateCompilation(compilation, out var outputCompilation, out var generateDiagnostics);
return (generateDiagnostics, outputCompilation.SyntaxTrees.Last().ToString());
}
6. Hello World
6.1 Program.cs
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
HelloWorldGenerated.HelloWorld.SayHello();
}
}
6.2 HelloWorldGenerator.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.CodeAnalysis;
using Microsoft.CodeAnalysis.Text;
namespace SourceGeneratorSamples
{
[Generator]
public class HelloWorldGenerator : ISourceGenerator
{
public void Execute(GeneratorExecutionContext context)
{
// begin creating the source we'll inject into the users compilation
StringBuilder sourceBuilder = new StringBuilder(@"
using System;
namespace HelloWorldGenerated
{
public static class HelloWorld
{
public static void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine(""Hello from generated code!"");
Console.WriteLine(""The following syntax trees existed in the compilation that created this program:"");
");
// using the context, get a list of syntax trees in the users compilation
IEnumerable<SyntaxTree> syntaxTrees = context.Compilation.SyntaxTrees;
// add the filepath of each tree to the class we're building
foreach (SyntaxTree tree in syntaxTrees)
{
sourceBuilder.AppendLine($@"Console.WriteLine(@"" - {tree.FilePath}"");");
}
// finish creating the source to inject
sourceBuilder.Append(@"
}
}
}");
// inject the created source into the users compilation
context.AddSource("helloWorldGenerated", sourceBuilder.ToString());
}
public void Initialize(GeneratorInitializationContext context)
{
// No initialization required
}
}
}
6.3 实际生成的文件 helloWorldGenerated.cs
using System;
namespace HelloWorldGenerated
{
public static class HelloWorld
{
public static void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello from generated code!");
Console.WriteLine("The following syntax trees existed in the compilation that created this program:");
Console.WriteLine(@" - Program.cs");
}
}
}
